Arthritis
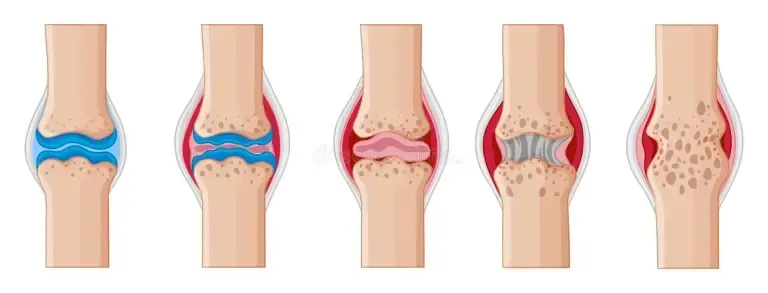
Arthritis is a disease which involves inflammation or degeneration of joints of the body, causing pain and difficulty to move or stay active.
Osteoarthritis is a progressive, degenerative joint disease affecting one or multiple joints. It is associated with risk factors including overweight, obesity, history of joint injury or surgery, genetic predisposition and aging.
Pharmaceutical treatment of arthritis involves analgesics, glucocorticoids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Optimal treatment of arthritis features a multidisciplinary approach involving patient education in self-management, occupational therapy and exercise.
Types of arthritis
Arthritis is an ‘umbrella term’ that describes over 100 different joint conditions. The most common ones include the following:
- Osteoarthritis – most common form – cartilage in the joints breaks down from repeated stress
- Rheumatoid arthritis – a disease that causes the immune system to attack synovial membranes in the joints and may affect vital organs
- Ankylosing spondylitis – arthritis of the spine, usually present in the lower back
- Gout – hard crystals are formed in the joints caused from high uric acid levels
- Psoriatic arthritis – inflammation in the joints develops in persons that already have an autoimmune disorder that can also cause skin irritation
- Juvenile arthritis – a disorder where the immune system attacks the tissues around joints. This is typically present in children 16 and younger
Movement as Medicine
Types of exercises include:
- Low-impact aerobic activities
- Muscle-strengthening exercises
- Flexibility exercises
- Balance and proprioception exercises
Exercise is essential for managing the conditions mentioned above. For instance, if physical activity is reduced, the disease can continue to get worse. Studies have shown that majority of These individuals are more likely to have muscle wasting and may be overweight compared to healthy individuals their age and sex
- maintains and improves strength and aerobic capacity, thereby minimizing or preventing functional decline
- decreases joint stiffness
- aids in weight control and achieving a healthy body composition
- reduces comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and
- improves mental health and quality of life
Range of Motion
Range of motion is the ability to move your joints through the full motion they were designed to achieve. These exercises include gentle stretching and movements that take joints through their full span. Doing certain exercises regularly can help maintain and improve the flexibility in the joints.
When joint damage and loss of mobility is severe, and restoration of a reasonable level of function and control of pain is no longer achievable by pharmacological and conservative management, total joint replacement and other surgeries are increasingly becoming routine options.
Arthritis can not be cured, but we can most definitely maintain and improve your current level of activity and manage the symptoms, aches and pains through individualized exercise, stretching programs.






